LXD
If your host does not have an IPV6 subnet and you want to assign IPV6 addresses to containers, then please check the Customize partition in the LXD module for the Attach a free IPV6 address segment to the host, and attach an IPV6 subnet to the host before installing the environment.
Setting up virtual memory (SWAP) (optional, not required)
TIP
Memory to open some swap lest the machine blow up, if your host computer does not have enough memory and a lot of free hard disk.
Unit conversion: Enter 1024 to generate 1G SWAP-virtual memory, virtual memory occupies hard disk space.
When the actual memory is not enough, the virtual memory will be automatically used for memory usage, but it will bring high IO usage and CPU performance.
Refer to the description of the organization's related project Jump This opens the size of virtual memory
| Physical Memory Size | Recommended SWAP Size |
|---|---|
| ≤ 2G | 2x memory size |
| 2G < memory ≤ 8G | Equal to physical memory |
| ≥ 8G | About 8G is sufficient |
| Hibernation needed | At least equal to physical memory |
The above values are only recommended settings, the actual value according to their own needs, do not blindly copy the value!
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spiritLHLS/addswap/main/addswap.sh -o addswap.sh && chmod +x addswap.sh && bash addswap.shLXD One-Click Installation Guide
WARNING
If this is a new server, make sure that both apt update and apt install curl are working properly before executing this script.
TIP
It's recommended to wait for at least 5 minutes after the system boots up before executing the following commands. This is to avoid the script being executed by the default system settings, which could cause issues with apt sources.
- Prerequisites: Ubuntu 18+ (recommended), Debian 8+ (Incus more recommended)
- During installation, you will be prompted to enter the storage pool creation path as well as the size, and all the VMs or containers you want to open end up taking up space in the storage pool
- The server needs to be restarted after the environment installation process to load some default configurations
- By default, lxd's lxcfs-related configuration is enabled, so that in-container querying of container information changes to information about the container itself rather than the host
- This installer has been tested to work on either physical or non-physical machines
Command:
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/oneclickvirt/lxd/main/scripts/lxdinstall.sh -o lxdinstall.sh && chmod +x lxdinstall.sh && bash lxdinstall.shOR
bash lxdinstall.shExample of initialization configuration:
If you don't need to specify the path of a non-system disk as the default storage pool, then you can directly enter or type n when choosing whether to customize the storage pool path, and you don't need to specify the path.
If you need to specify the path of a non-system disk as the default pool, then you need to select y and enter the corresponding path (the actual absolute path of the disk you mounted).
If the corresponding disk has 18 Gigabytes of free hard disk space in addition to the occupied space and you want to open a 15 Gigabyte storage pool, follow the command line prompts to enter 15.
WARNING
If you need to open more than 200 LXD containers on a single server, then it is not recommended to use this project, there may be problems with lxcfs access drift, which generates IO occupancy that cannot be released. (This is a native LXC problem that can't be fixed.)
Installation of WEB Control Panel
Customization There are tutorials on how to enable the official panel, but here do not choose to use the official panel, because the official panel in order to security, at the expense of a lot of user experience, this piece of using the
https://github.com/turtle0x1/LxdMosaic
third-party panels
sudo snap install lxdmosaicDo a straightforward one-click install, then open the current host's https://<public IP address>/ and force access to it to get to the setup page
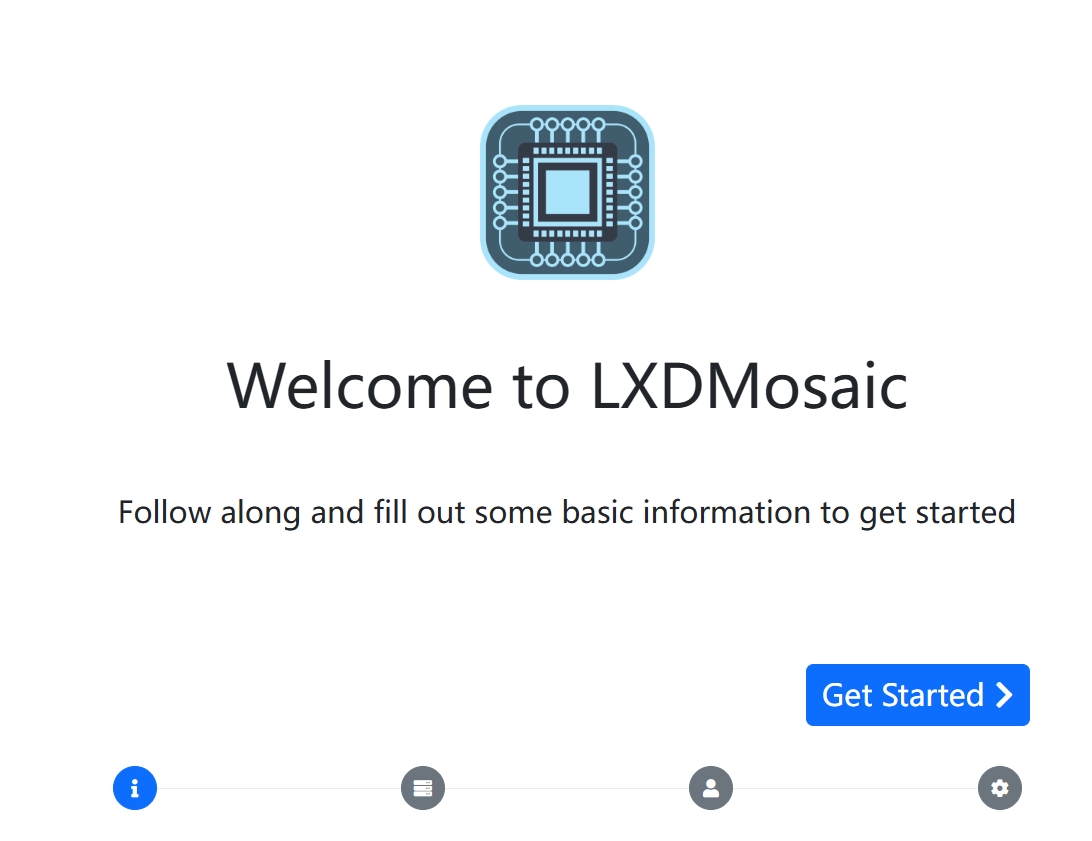
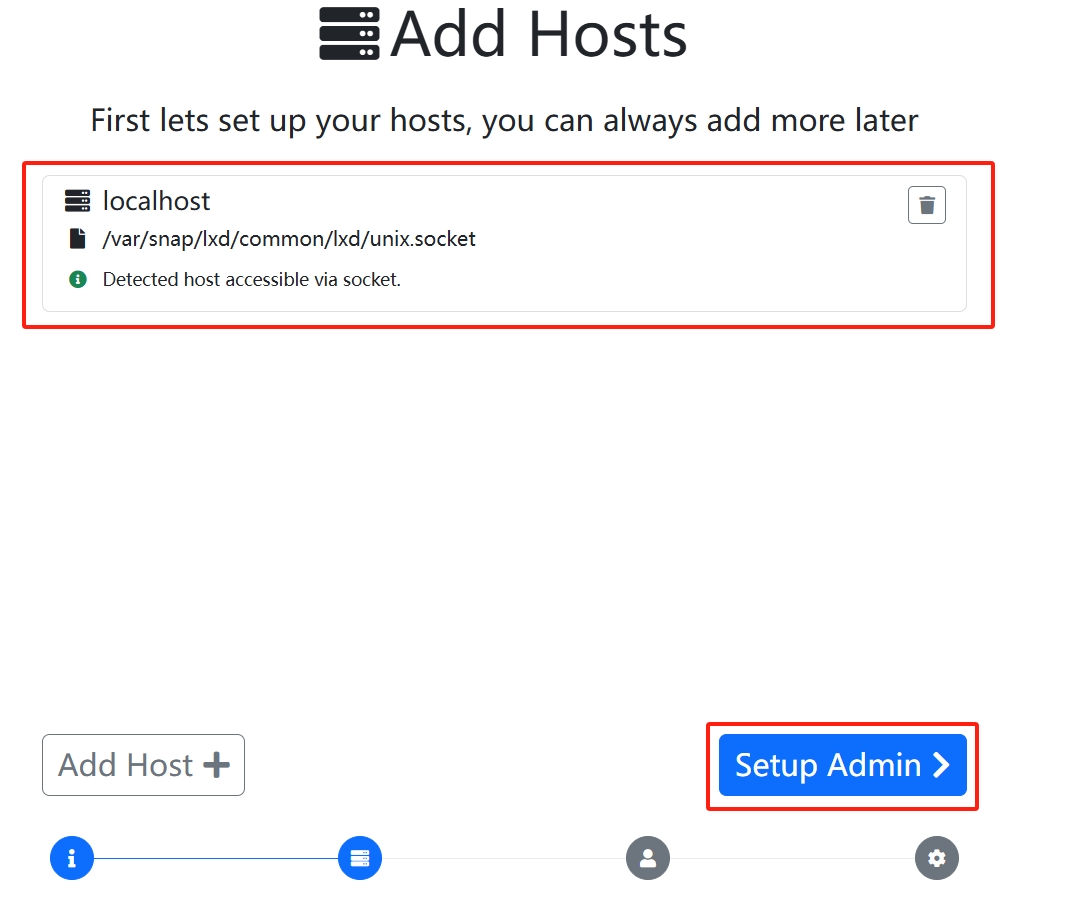
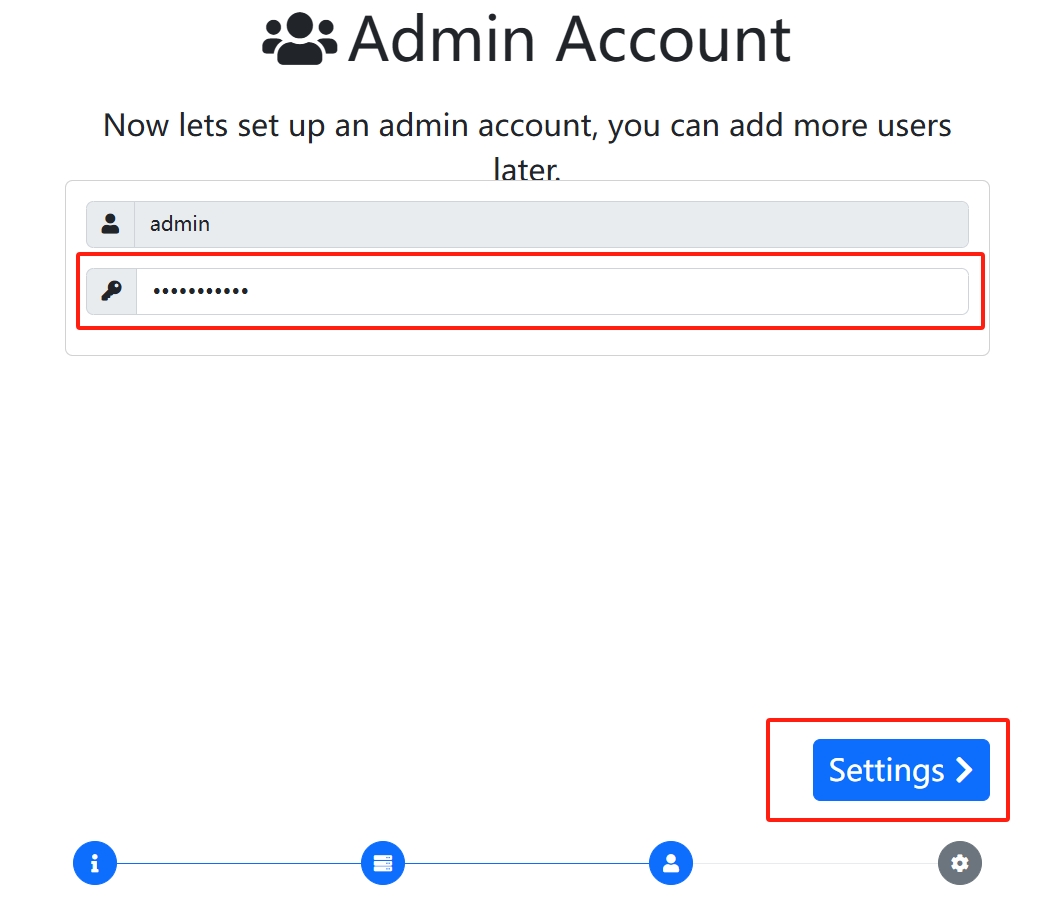
This piece can be changed if you need to set up the site name
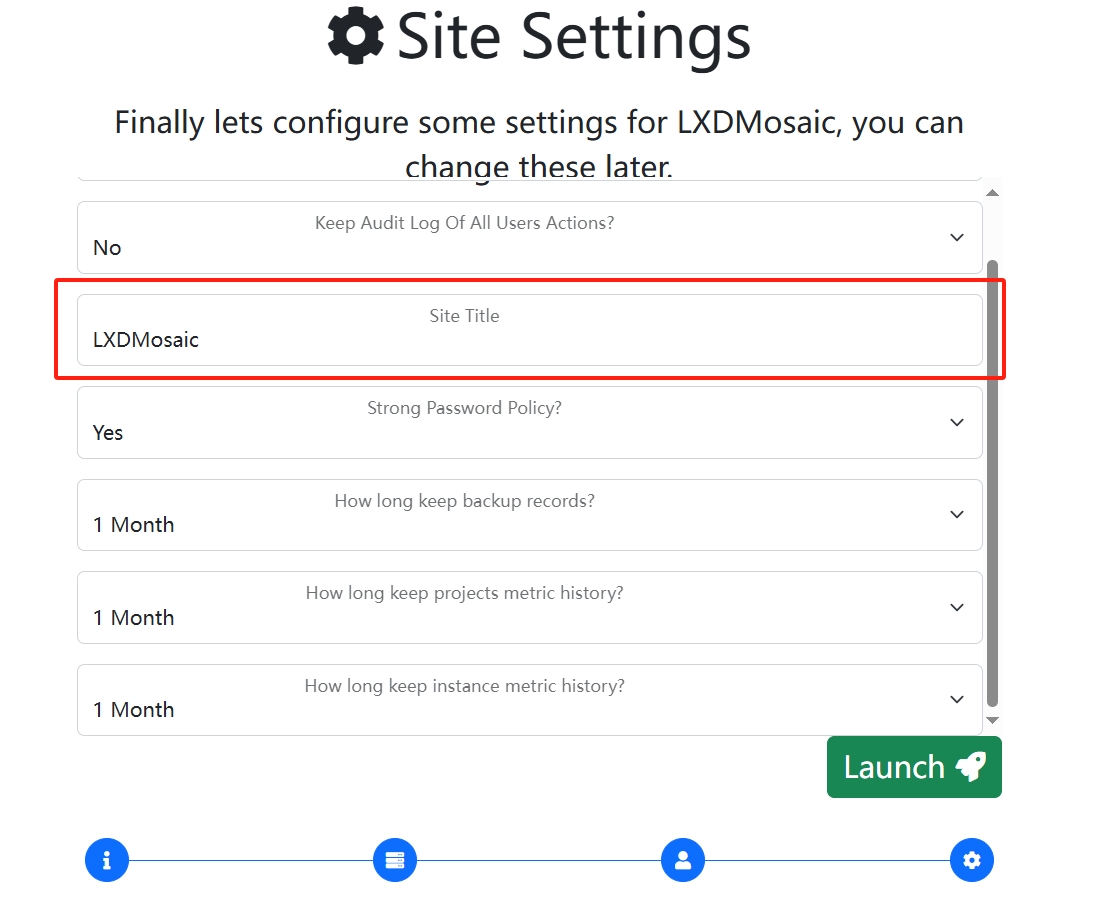
Better than nothing can only mean that there is no RBAC access control for sub-user segregation
Manual installation (optional)
Not recommended, just to install for some oddball environments where one-click scripts won't run, or if you want to understand the most basic LXD installation process.
Disable Firewall
apt update
apt install curl wget sudo dos2unix ufw jq -y
ufw disable2
3
Enabling Virtual Memory SWAP
The amount of memory depends on how many instances you want to run. If you want to run 8 instances and calculate, you'll need 2GB of memory. If your actual physical memory is 512MB, you'll need an additional 1.5GB. To be cautious, allocate 2GB of virtual memory.
Execute the following commands: Enter '1', then enter '2048'. This signifies allocating 2GB of virtual memory.
Command:
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/oneclickvirt/lxd/main/scripts/swap.sh -o swap.sh && chmod +x swap.sh && bash swap.shInstalling LXD
Actually, the virtual memory allocated for swap should be twice the size of the actual memory. So, it's reasonable to allocate 1GB if the actual memory is 500MB. The scenario I described above is an excessive allocation.
apt install snapd -y
snap install lxd
/snap/bin/lxd init2
3
If the following error occurs in the above command
(snap "lxd" assumes unsupported features: snapd2.39 (try to update snapd and refresh the core snap))
Use the command patch before installing lxd
snap install coreIf there are no exceptions, the results of the above three lines of commands are as follows
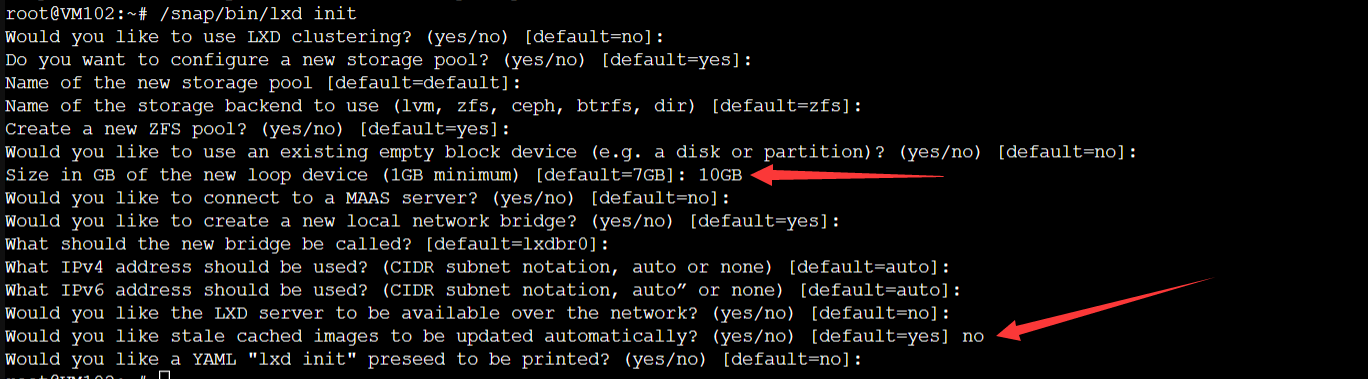
Just enter the default for the normal options
Choose the size of the physical disk (hint: select the default option with a minimum of 1GB). Generally, I fill in the available disk space minus the memory size, then multiply by 0.95 and round down. Here, I entered 10GB.
Remember to select 'no' for options containing 'auto' when prompted to update the image, in order to avoid occupying the system.
Test whether symbolic links are functioning in LXC.
lxc -hIf an error is reported then execute the following command to soft connect the lxc command
! lxc -h >/dev/null 2>&1 && echo 'alias lxc="/snap/bin/lxc"' >> /root/.bashrc && source /root/.bashrc
export PATH=$PATH:/snap/bin2
After connecting, test the lxc command again to see if there is an error about not being able to find it
